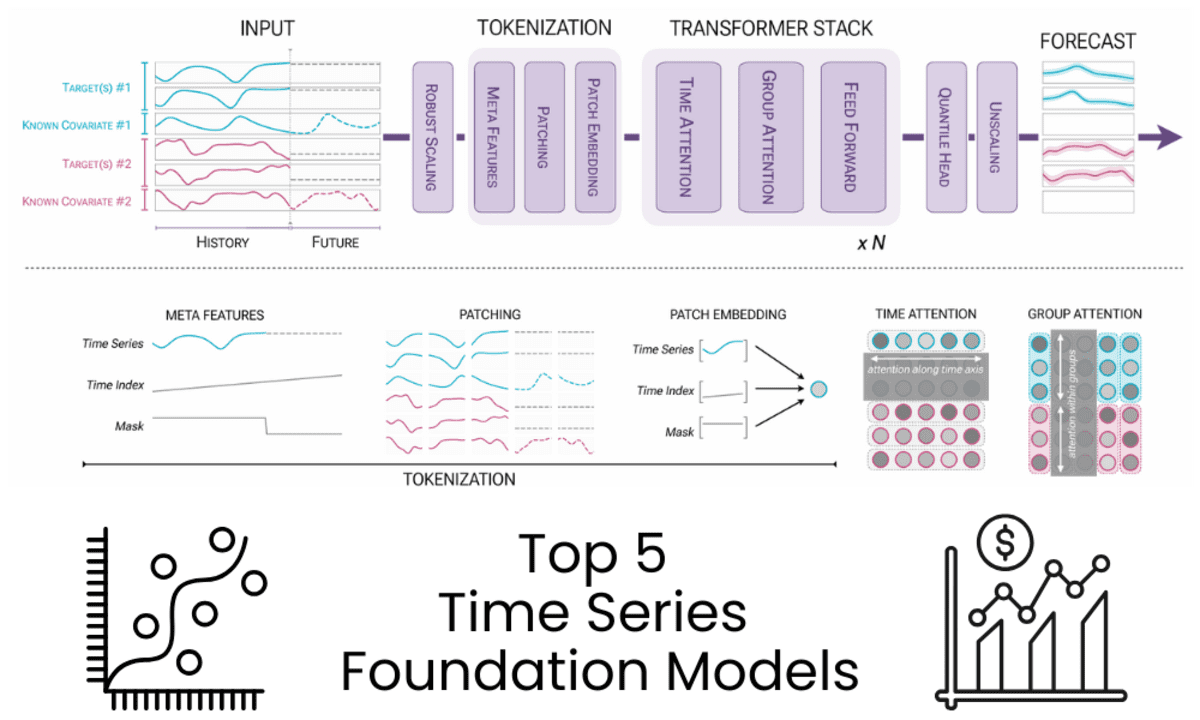
Photo by author From the diagram Chronos-2: From univariate to universal prophecy
# Introduction
The foundation models did not originate from Chat GPT. Long before large language models became popular, pre-existing models were already making advances in computer vision and natural language processing, including image segmentation, classification and text understanding.
The same approach is now being used to redefine time series forecasting. Rather than building and tuning a separate model for each dataset, Time Series Foundation models are projected onto large and diverse collections of temporal data. They can offer strong zero-shot forecasting performance across domains, frequencies and horizons, often matching deep learning models that require hours of training using only historical data as input.
If you’re still relying primarily on classical statistical methods or single-dataset deep learning models, you could be missing a big shift in how you build predictive systems.
In this tutorial, we examine five time-series foundation models, selected based on performance, popularity of face-hugging measurement of downloads, and real-world use.
# 1. Chronos-2
Chronos-2 A 120m parameter, Encoder is the only time-series foundation model built for zero-shot forecasting. It supports univariate, multivariate, and covariate-aware prediction in a single architecture and offers accurate multivariate probability prediction without task-specific training.
Key Features:
- Encoder-only architecture inspired by T5
- Predicting zero shot with quantile output
- Local support for the harmony of the past and the known future
- Long context lengths up to 8,192 and horizon predictions up to 1,024
- Evaluation of efficient CPU and GPU with high throughput
Use cases:
- Many related time series are widely predicted
- Covariate-driven forecasting such as demand, energy, and pricing
- Rapid prototyping and production deployment without model training
Best use cases:
- Production forecasting systems
- Research and benchmarking
- Complex multivariate forecasting with covariates
# 2. Terrex
Tirex A 35 m parameter perimeter parameterized time series forecasting model based on XLSTM, designed for zero-shot forecasting at both long and short horizons. It can generate accurate predictions without any training on task-specific data and provides both point and probability predictions out of the box.
Key Features:
- Architecture based on pretrained XLSTM
- Zero-shot prediction without dataset-specific training
- Estimation of uncertainty based on point forecasts and quantiles
- Strong performance on both long- and short-horizon benchmarks
- Optional CUDA acceleration for high performance GPU evaluation
Use cases:
- Zero-shot forecasting for new or unseen time series datasets
- Long and short term forecasting in finance, energy and operations
- Fast benchmarking and deployment without model training
# 3. Time FM
Time FM A time series foundation developed by Google Research for zero-shot forecasting. Open Outpost Time FM-2.0-500M is a decoder-only model designed for asynchronous forecasting, supporting long historical contexts and flexible forecasting horizons without task-specific training.
Key Features:
- Decoder only foundation model with 500 meter parameter checkpoint
- Zero-Shot Univariate Time Series Forecasting
- Context length up to 2,048 time points, with support beyond the training threshold
- Flexible forecast horizon with optional frequency indicator
- Better for fast point prediction at scale
Use cases:
- Large-scale univariate prediction in heterogeneous datasets
- Long-horizon forecasting for operational and infrastructure data
- Rapid testing and benchmarking without model training
# 4. IBM Granite TTM R2
Granite Timers-TTM-R2 Tenny Temixers (TTM) is a family of compact, pretrade time series foundation models developed by IBM Research under the framework. Designed for multivariate prediction, these models achieve robust zero-shot and some-shot performance despite the small size of the model size of 1M parameters, making them suitable for both research and resource-constrained environments.
Key Features:
- Smaller models are starting with 1M parameters
- Robust zero-shot and few-shot multivariate forecasting performance
- Focused models according to specific contexts and prediction lengths
- Fast and fine-tuning on a single GPU or CPU
- Support for external variables and static class properties
Use cases:
- Multivariate forecasting in low-resource or edge environments
- Zero-shot baselines with optional lightweight fine-tuning
- Rapid deployment for operational forecasting with limited data
# 5. Full Open Base 1
Toto Open Base -1.0 A decoder is simply a time-series foundation model designed for multivariate forecasting in observational and monitoring settings. It is optimized for high-dimensional, sparse, and non-stationary data and offers strong performance on large-scale benchmarks such as gift crossing and zero-shot on boom.
Key Features:
- Decoder-only transformer for flexible context and prediction length
- Fine tuning with zero shot predictability
- Efficient handling of high-dimensional multivariate data
- Probability prediction using the Student-t mixture model
- Pre-processed over two trillion time series data points
Use cases:
- Observation and forecasting of monitoring metrics
- High-dimensional systems and infrastructure telemetry
- Zero-shot forecasting for large-scale, non-stationary time series
Summary
The table below compares the main features of time series foundation models focusing on model size, architecture and forecasting capabilities.
| Model | Parameters | Architecture | Type of prediction | Key Strengths |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Chronos-2 | 120m | Encoder only | Univariate, multivariate, probabilistic | Strong zero shot accuracy, long context and horizon, high individuality input |
| Tirex | 35 meters | Based on XLSTM | Immutable, probabilistic | Lightweight model with strong short- and long-distance performance |
| Time FM | 500 meters | Decoder only | Unbiased, point forecast | Handles long contexts and flexible horizons at scale |
| Granite Timeseries TTM-R2 | 1M – less | Focusing models | Multivariate, point prediction | Extremely compact, fast, strong zero- and few-shot results |
| Toto Open Base 1 | 151 m | Decoder only | Multidimensional, probabilistic | Optimized for high-dimensional, non-stationary observational data |
Abid Ali Owan For centuries.@1abidaliawan) is a certified data scientist professional who loves building machine learning models. Currently, he is focusing on content creation and writing technical blogs on machine learning and data science technologies. Abid holds a Master’s degree in Technology Management and a Bachelor’s degree in Telecommunication Engineering. His vision is to create an AI product using graph neural networks for students with mental illness.

